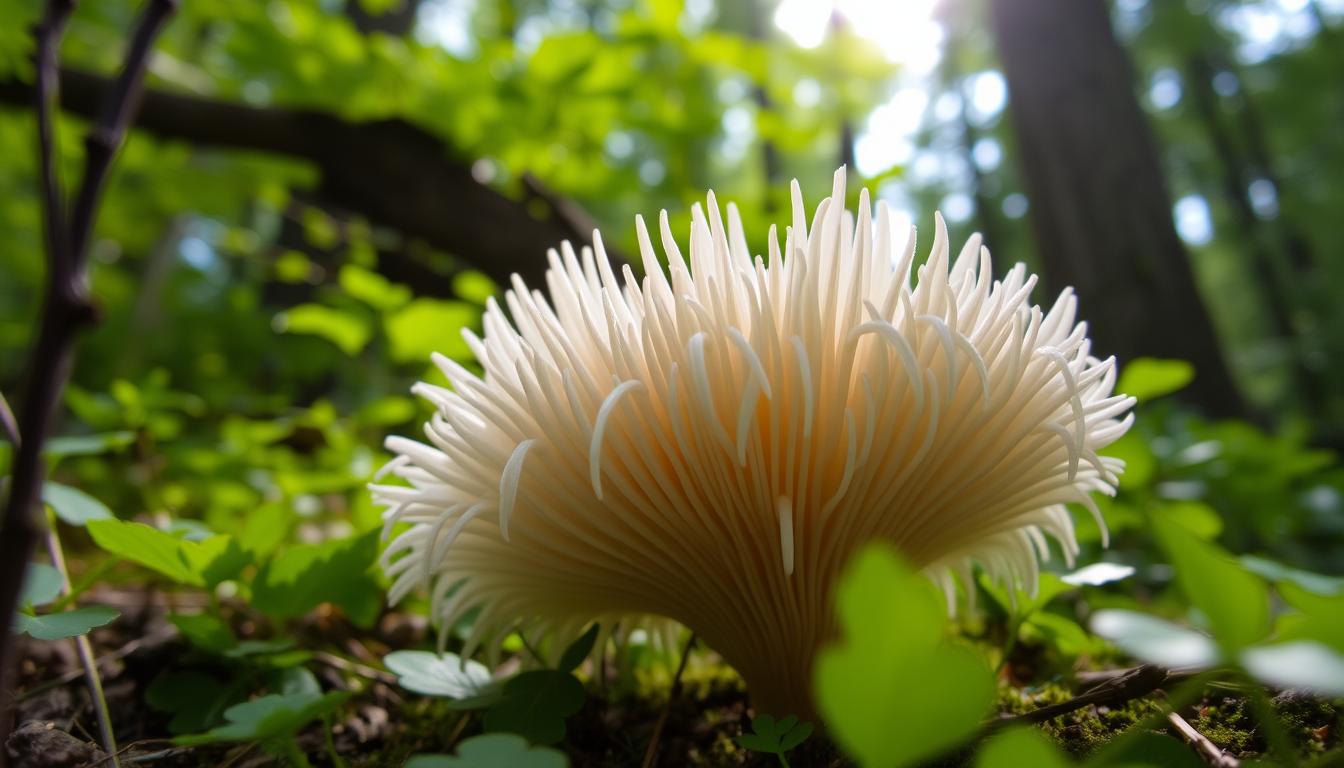
Lion’s mane mushrooms (Hericium erinaceus) are white, shaggy mushrooms that resemble a lion’s mane. These fascinating fungi have been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries and are now gaining widespread attention for their potential to promote brain health and cognitive function. Containing a unique array of bioactive compounds, lion’s mane mushrooms may stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF), enhance memory and focus, and even protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Widely consumed across Asia, these “smart mushrooms” can be enjoyed in a variety of forms, from raw and cooked to dried powders, liquid extracts, and dietary supplements. As research continues to unveil the remarkable benefits of lion’s mane, this ancient superfood is quickly becoming a popular natural solution for those seeking to support brain health and cognitive performance.
Key Takeaways
- Lion’s mane mushrooms contain compounds that may enhance cognitive function, memory, and focus.
- These mushrooms exhibit neuroprotective properties and can potentially aid in the prevention or treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Lion’s mane may also offer mental health benefits, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- The mushrooms can be consumed in various forms, including raw, cooked, dried, and as supplements.
- Ongoing research continues to uncover the diverse health benefits of this remarkable “smart fungus”.
Understanding Lion’s Mane Mushroom: An Introduction to the Smart Fungus
The captivating Hericium erinaceus, commonly known as the Lion’s Mane mushroom, has a rich history in Eastern medicine. This remarkable fungus has been utilized for centuries, particularly in traditional Chinese and Japanese practices, for its potential health benefits.
Traditional Uses in Eastern Medicine
In traditional Chinese medicine, the Lion’s Mane mushroom has been revered for its restorative and tonic properties. It has been used to support various aspects of well-being, including cognitive function, immune system, and overall vitality. The mushroom’s unique appearance, with its long, flowing tendrils resembling a lion’s mane, has contributed to its traditional moniker and esteemed status in Eastern cultures.
Scientific Name and Physical Characteristics
Scientifically known as Hericium erinaceus, this medicinal mushroom boasts a distinctive appearance. Its long, cascading white tendrils give it a striking resemblance to a lion’s mane, earning it the popular name “Lion’s Mane.” This unique fungus is native to temperate forest regions in North America, Europe, and Asia, thriving on the decaying wood of hardwood trees.
Natural Habitat and Cultivation
The Lion’s Mane mushroom can be found growing naturally in the wild, particularly in the temperate forest regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. However, due to increasing demand, commercial cultivation of this medicinal mushroom has become more widespread. The cultivation process often involves growing the mushrooms on sawdust or other organic substrates, allowing for a reliable supply of this valuable natural resource.

“The Lion’s Mane mushroom has been used in Eastern medicine for centuries, valued for its potential to support cognitive function and overall well-being.”
The Science Behind Lion’s Mane Mushroom Benefits for Brain Health
Emerging scientific research suggests that lion’s mane mushrooms contain compounds that may promote neuroprotection, cognitive function, and brain cell regeneration. These remarkable fungi have shown promising potential in improving memory, focus, and overall brain health.
Studies indicate that lion’s mane extracts may stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF), a crucial protein for the growth and maintenance of neurons. This property could have far-reaching implications for treating neurodegenerative diseases and enhancing cognitive performance.
In one study, 41 healthy adults aged 18-45 were randomly assigned to either a placebo group or a group receiving 1.8g of Hericium erinaceus (lion’s mane). The results showed a trend towards reduced subjective stress following 28-day supplementation with lion’s mane.
Additionally, a single dose of lion’s mane was found to improve participants’ performance on the Stroop task, a test of cognitive function, within 60 minutes of administration.
“Preliminary research observed improvements in scores of mild cognitive impairment in 50- to 80-year old adults following 16 weeks of 3g/day Hericium erinaceus supplementation.”
However, the research is not entirely conclusive, as some studies have not found cognitive benefits in younger adult populations. Nonetheless, the potential for lion’s mane to support brain health and neural regeneration remains a promising area of study.
| Study Population | Dosage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Menopausal women | 4 weeks of Hericium erinaceus-containing cookies | Lowered depression and anxiety scores |
| Overweight and obese adults | 8 weeks of Hericium erinaceus supplementation | Reduced depression, anxiety, and sleep disorder scores |
| College-age athletes | 4 weeks of 10g/day Hericium erinaceus | No cognitive effects observed |
While the research on lion’s mane’s benefits for brain health is promising, more human studies are needed to fully understand the extent of its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. Nevertheless, the existing evidence suggests that this humble mushroom may hold the key to supporting healthy brain function and neural regeneration.

Key Bioactive Compounds in Lion’s Mane
Lion’s mane mushrooms, known for their remarkable brain-boosting properties, contain a treasure trove of unique bioactive compounds. Two of the most notable are hericenones and erinacines, which work in synergy to support cognitive function and neural growth.
Hericenones and Their Role
Hericenones are found in the fruiting body of the lion’s mane mushroom. Research has shown that these compounds can stimulate the synthesis of nerve growth factor (NGF), a crucial protein that promotes the growth and repair of nerve cells. A 2012 study found that lion’s mane mushrooms had the fourth highest antioxidant activity among 14 types of mushrooms evaluated, described as “moderate to high.”
Erinacines and Neural Growth
Erinacines, present in the mushroom’s mycelium, have the remarkable ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and further enhance neural growth. Studies on rats have revealed that erinacine A can prevent cell death and protect against neuron damage in the brain, making it a promising neuroprotective agent.
Other Important Compounds
In addition to hericenones and erinacines, lion’s mane mushrooms contain other valuable bioactive compounds, such as polysaccharides and beta-glucans. Polysaccharides have been shown to possess antioxidant and immune-boosting properties, while beta-glucans are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.

“Erinacines and hericenones were revealed as small molecules with significant neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects, showing potential for crossing the blood-brain barrier.”
The synergistic action of these bioactive compounds in lion’s mane mushrooms make them a valuable natural resource for supporting brain health and cognitive function.
Cognitive Enhancement and Memory Improvement
Mounting evidence suggests that the remarkable lion’s mane mushroom may hold the key to enhanced cognitive function and improved memory. Researchers from The University of Queensland have uncovered active compounds within this “smart fungus” that possess remarkable neuroprotective and neurotrophic properties, promoting neural growth and boosting memory formation.
Preclinical trials have shown that the active compounds from lion’s mane have a significant impact on brain cell growth and memory improvement. The study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry highlighted that these mushroom-derived compounds enhanced spatial memory through a unique pan-neurotrophic pathway, activating ERK1/2 signaling and leading to improved cognitive performance.
The research also demonstrated that Hericene A, a derivative from lion’s mane, led to increased neurotrophin expression and downstream signaling, resulting in significantly enhanced hippocampal memory. This memory enhancement potential was correlated with the activation of ERK1/2 signaling, showcasing a novel mechanism for cognitive improvement.
But the benefits of lion’s mane don’t stop there. Cognitive tests have shown significant improvement in attention and processing skills just 48 hours after taking this remarkable mushroom. Moreover, subjective stress levels decreased notably after a 28-day intervention with lion’s mane in a study involving 41 healthy adults.
These findings suggest that lion’s mane could be a powerful focus booster, memory enhancement, and cognitive function ally, providing a natural edge for those seeking to optimize their mental performance. As the research continues to unfold, the potential of this “smart fungus” to revolutionize brain health and cognitive enhancement becomes increasingly clear.
“The study emphasized the need for further research with larger sample sizes to improve the validity and reliability of the findings. However, the potential of lion’s mane mushroom for cognitive performance supplements aimed at young adults seeking a mental edge is undeniable.”
Neuroprotective Properties and Brain Cell Regeneration
The lion’s mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) has shown remarkable neuroprotective abilities, making it a promising natural solution for supporting brain health. Its active compounds, such as erinacines and hericenones, have been extensively researched for their potential to safeguard the nervous system and promote neural regeneration.
Protection Against Neurodegenerative Diseases
Studies have revealed that lion’s mane extracts can reduce the symptoms of memory loss and prevent neuronal damage caused by amyloid-beta plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. The mushroom’s neuroprotective properties may help slow or even prevent the progression of neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases.
Neural Growth Factor Stimulation
One of the key mechanisms by which lion’s mane benefits the brain is its ability to stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF). NGF is a critical neurotrophic factor that plays a crucial role in the survival, growth, and differentiation of neurons. The mushroom’s compounds, such as hericene A and N-de phenylethyl isohericerin (NDPIH), have been shown to increase NGF synthesis and promote the regeneration of damaged nerve cells.
Additionally, lion’s mane has been found to boost the levels of other important neurotrophins, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin 3 (NT3), and neurotrophin 4/5 (NT4/5). These neurotrophic factors are crucial for neuronal survival, neurite outgrowth, and dendritic branching, which are essential for cognitive function and overall brain health.
“The lion’s mane mushroom exhibits remarkable neuroprotective properties, making it a promising natural solution for supporting brain health and preventing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.”
Ongoing research on the neuroprotective and neuroregenerative potential of the lion’s mane mushroom holds great promise for the development of innovative natural therapies targeting a wide range of neurological and cognitive disorders.
Mental Health Benefits: Depression and Anxiety Relief
Lion’s mane mushrooms have shown promising potential in improving mental health, particularly in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. According to a study published in the Journal of Molecular Science, the mushroom may serve as a potential alternative treatment for depression.
Researchers have found that individuals with major depressive disorder tend to have lower nerve growth factor levels compared to non-depressed individuals, as highlighted in a 2015 meta-analysis in Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. The neuroprotective and nerve growth-stimulating properties of lion’s mane mushroom may contribute to its mood-enhancing effects.
A placebo-controlled trial in Phytotherapy Research demonstrated that lion’s mane improved symptoms of mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 50 to 80 who took the supplement for 16 weeks. Additionally, a 2021 study in Antioxidants revealed promising research on the use of lion’s mane for traumatic brain injury, suggesting potential neuroprotective effects.
In a 2010 study in Biomedical Research, participants who consumed lion’s mane reported less anxiety after four weeks compared to those who had a placebo. Similarly, a 2018 study found that lion’s mane extract had an antidepressant effect on stressed-out mice after 14 days of use.
The positive effects of lion’s mane on mental health may be attributed to factors like increased neurotransmitters in the hippocampus and a reduction of brain inflammation, as noted by researchers. Another 2018 study in mice found that lion’s mane mushroom promoted the production of new brain cells in the hippocampus after just 4 weeks of once-a-day treatment, which may be behind its anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects.
“Lion’s mane mushroom is a potential alternative treatment for depression, as highlighted in a 2020 abstract in the Journal of Molecular Science.”
While the existing research on lion’s mane mushroom’s mental health benefits is promising, more extensive human studies are needed to confirm these findings and understand the mechanisms behind the potential mood-enhancing properties of this remarkable fungus.

Nerve Growth and Repair Properties
Lion’s mane mushroom has shown promising effects in promoting nerve growth and repair, which could be particularly beneficial for various nervous system injuries and conditions. Research has demonstrated that compounds extracted from the lion’s mane fungus can accelerate the regeneration of damaged nerves and potentially reduce recovery time from nerve injuries.
Impact on Nervous System Recovery
Studies have revealed that active compounds found in lion’s mane, such as hericene A and NDPIH, can stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF) and enhance the growth and branching of neurons. This property may be especially useful in treating conditions like peripheral neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes that involves nerve damage.
Benefits for Nerve Damage
The ability of lion’s mane mushroom to cross the blood-brain barrier and its neuroprotective effects make it a potential candidate for supporting overall nervous system health. In animal studies, dietary supplementation with lion’s mane extract has been shown to significantly enhance recognition memory and improve outcomes in models of nerve injury and neurodegenerative diseases.
While more research is needed to confirm the safety and efficacy of lion’s mane mushroom extracts for human use, the current evidence suggests that this “smart fungus” may offer promising nerve regeneration and repair properties that could be beneficial for a range of neurological conditions and injuries.
| Compound | Effect on Neurons | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hericene A | Promotes neuritogenesis (growth and branching of neurons) | Memory enhancement, nerve regeneration |
| NDPIH | Stimulates nerve growth factor (NGF) production | Neuroprotection, nerve repair |
| Lion’s Mane Crude Extract | Enhances recognition memory in animal studies | Potential benefits for neurological conditions and injuries |
The research on lion’s mane mushroom’s nerve growth and repair properties is still ongoing, and further investigation is needed to fully understand its potential applications and safety profile. However, the current evidence suggests that this versatile fungus may offer a natural solution for supporting nervous system health and recovery.
Different Forms and Consumption Methods
The versatility of lion’s mane mushrooms extends beyond their culinary uses. These remarkable fungi are available in various forms, catering to different preferences and health needs. From fresh to dried, powdered to supplemental extracts, there’s an option to suit every lifestyle.
Fresh lion’s mane mushrooms can be savored as a culinary delight, with a delicate flavor often likened to seafood. Dried mushrooms can be rehydrated and incorporated into soups, stews, or sautéed dishes. For those seeking a more concentrated form, powdered lion’s mane can be easily added to beverages, smoothies, or even sprinkled onto meals to unlock its beneficial compounds.
Supplements offer another convenient way to incorporate this versatile mushroom into your daily routine. Lion’s mane supplements are available as liquid extracts or encapsulated powders, providing a concentrated dose of the mushroom’s active compounds. These options can be particularly beneficial for those seeking targeted cognitive or neurological support.
Regardless of the form, the key is to find the consumption method that best aligns with your preferences and health goals. Whether you choose to savor the fresh mushroom, sip a lion’s mane-infused tea, or incorporate the powdered form into your culinary creations, the potential benefits of this remarkable fungi are within reach.
“Lion’s mane mushrooms are a true superfood, offering a wealth of potential benefits for cognitive function, nerve health, and overall well-being. Exploring the different forms and consumption methods can help you unlock the full potential of this remarkable fungus.”
Optimal Dosage and Timing Recommendations
The optimal dosage for lion’s mane mushrooms can vary depending on the form and intended use. Studies have explored a range of doses, from as low as 250 milligrams to as high as 3 grams per day. For cognitive benefits, some research has utilized 3 grams of powdered lion’s mane daily, while others have used 1 gram of extract.
Daily Recommended Intake
It’s generally recommended to start with a lower dose and gradually increase as needed. The Real Mushrooms brand suggests 1 gram of powdered extract per day as a suitable daily dosage for the average person. Dried lion’s mane powder is often consumed at 1 to 2 grams per day, while extract supplements commonly range from 300 milligrams to 1 gram per day, divided into two or three doses.
Best Times for Consumption
The timing of lion’s mane consumption may depend on individual goals and preferences. Many people choose to take lion’s mane supplements in the morning for potential cognitive enhancement, while others prefer to consume it in the evening for possible sleep benefits. As with any supplement, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new regimen to ensure safety and optimal results.
FAQ
What are the brain health benefits of lion’s mane mushroom?
How have lion’s mane mushrooms been used in traditional medicine?
What are the key bioactive compounds in lion’s mane mushrooms?
Can lion’s mane mushrooms improve cognitive function and memory?
Do lion’s mane mushrooms have neuroprotective properties?
Can lion’s mane mushrooms help with mental health conditions?
How can lion’s mane mushrooms be consumed?
What is the recommended dosage for lion’s mane mushrooms?
Source Links
- What Are the Health Benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushrooms?
- 5 Lion’s Mane Mushroom Benefits
- 9 Health Benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushroom (Plus Side Effects)
- LION’S MANE MUSHROOM: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews
- The Acute and Chronic Effects of Lion’s Mane Mushroom Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Stress and Mood in Young Adults: A Double-Blind, Parallel Groups, Pilot Study
- The Acute and Chronic Effects of Lion’s Mane Mushroom Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Stress and Mood in Young Adults: A Double-Blind, Parallel Groups, Pilot Study
- Latest Study Suggests Lion’s Mane Mushrooms May Boost Brain Health
- Lion’s mane mushrooms: Benefits and side effects
- Chemical Constituents from Hericium erinaceus Promote Neuronal Survival and Potentiate Neurite Outgrowth via the TrkA/Erk1/2 Pathway
- Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of Lion’s Mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) from different growth periods
- Mushrooms Magnify Memory by Boosting Nerve Growth – Neuroscience News
- Mushrooms for the mind: Research concludes Lion’s Mane improves cognitive performance and reduces stress
- Neurotrophic and Neuroprotective Effects of Hericium erinaceus
- Lion’s Mane and the brain: Study identifies new compounds in ‘smart mushroom’
- Health Benefits Of Lion’s Mane
- Lion’s Mane Mushroom Benefits
- Lion’s Mane – LiverTox – NCBI Bookshelf
- Active compound in Lion’s Mane mushroom improves nerve growth and memory
- Lion’s mane mushrooms may help improve memory, boost brain cell growth
- Lion’s Mane: Benefits for Inflammation, Memory, and More
- Determining the Right Lion’s Mane Dosage for Optimal Health